This research proposed a novel method in the electrochemical injection of corrosion inhibitors (EICI) using imidazolium-based ionic liquids and Ce(III) as a pH-sensitive pore-blocking compound to reduce rebar corrosion and increase the sustainability of the in-use chloride-contaminated reinforced cementitious materials.
The analytical approach was conducted on the simulated concrete pore solution and mortar media for 360 days.
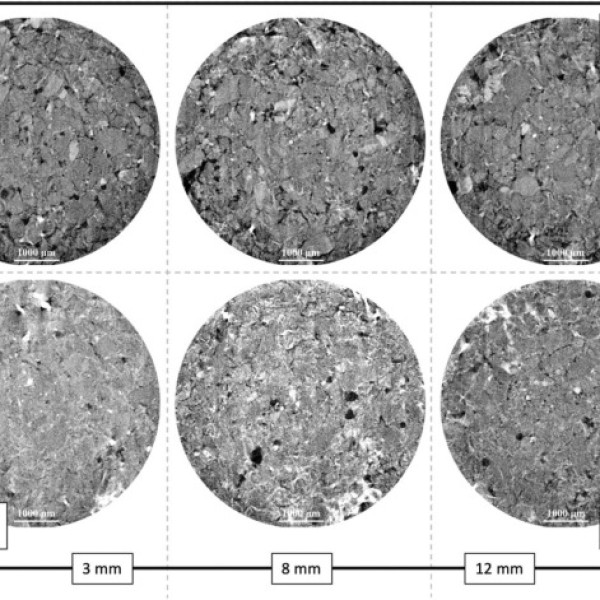
Compared to the typical EICI approach, our boosted EICI rehabilitation approach improved long-term performance by almost 90%. The volumetric analysis demonstrated that by precipitating Ce-rich compounds, the Ce (III) injection reduced the number and size of porosities while lowering 15% of the interconnected pores.